In the last few years, blockchain technology has been rapidly gaining traction as a game-changer in many sectors with potential to improve security, transparency, and efficiency. Meanwhile, for many, the notion of space remains in the dark. Here we are going to explore how blockchain basics ,how it works in simple terms and to understand why it is called the technology of the future.
What is Blockchain Technology?
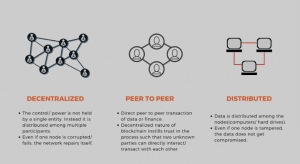
At the heart of the blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that carries out transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction (or block) is encrypted and linked to the previous one, this way building a chain. This decentralization therefore means that there is no need for intermediaries, like banks or government bodies, for the trust and transparency to be maintained.
Key Components of Blockchain
Decentralization
In contrast to the conventional centralized systems where data is stored in a single point, blockchain is based on a distributed network of nodes. This decentralization improves security by eliminating single points of failure and generally reducing the chance of tampering or fraud.
Cryptographic Hashing
The blockchain implements the cryptographic hashing to encrypt the data stored within each block. Every block has its own digital fingerprint, which is a cryptographic hash that is created with the help of complex mathematical algorithms. Any change in the data would yield a new hash, which would set off an alarm in the network, warning about any possible tampering.
Consensus Mechanisms
To support transactions and ensure the integrity of the ledger, the blockchain uses consensus mechanisms. Different blockchain networks have their own mechanisms which may consist of Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). These protocols are the ways through which the participants in the net reach the common ground about the legitimacy of the transactions.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is no longer limited to only cryptocurrency, as it has found applications in a variety of industries.
Finance: In the financial industry, blockchain technology enables quicker and safer cross-border payment transactions, reduces fraud in supply chain finance, and allows the creation of financial instruments such as smart contracts.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain in supply chains supports transparency and traceability by storing the movement of products from the manufacturer to the final consumer. The use of transponders leads to the guarantee of authenticity, the reduction of counterfeiting, and the ease of recalls.
Healthcare: In healthcare, blockchain secures patient data, simplifies the medical record management, and promotes interoperability among healthcare providers, thus, increases patient care and data accuracy.
Real Estate: Blockchain technology is changing the real estate industry by offering a secure and transparent platform for property transactions. Smart contracts executed on blockchain networks act as automatons, which simplify property transfers, title deeds, and escrow services, by eliminating paperwork, minimizing fraud, and speeding up transactions.
In a nutshell, blockchain technology paves the way for a new paradigm in data storage, management and transactions. Through blockchain comprehension, individuals and organizations can tap into its power to spur innovations and revolutions across different fields.